Shoreline Erosion
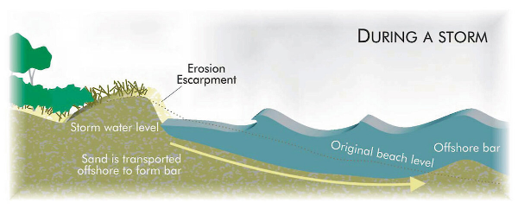
Shoreline erosion is the loss or displacement of land or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, and storm surges. Erosion is a natural part of the rock cycle but can cause extreme damages to structures and the land. There are ways to slow down shoreline erosion and possibly prevent further damages. To maintain soil stability and prevent erosion, consider implementing the following practices:
- Establish grass, shrubs, trees, or other ground cover to stabilize and hold soil in place.
- Apply mulch, rocks, or ripraps to shield the soil surface from water and wind erosion.
- Use mulch matting, fiber logs, or retaining walls to stabilize slopes and prevent landslides.
- Use a drainage system and reduce watering to prevent soil saturation and subsequent erosion.
- Avoid overgrazing, soil compaction, and excessive disturbance to protect soil integrity.
- Cover storm sewer inlets with straw or silt fences to prevent sediment from entering the drainage system.
Shoreline Erosion Solutions
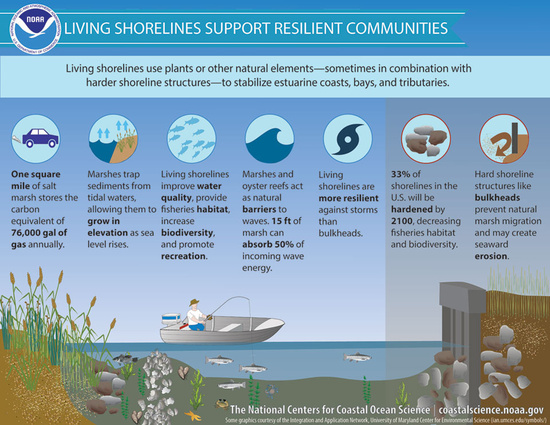
One recommended solution to shoreline erosion is the implementation of a living shoreline. Living shorelines use plants or other natural elements to create a barrier to protect the shore from waves.